Bluetooth Technology powers the wireless world around us, from earbuds and smartwatches to smart homes and healthcare devices.
Today, it is faster, more precise, and more versatile than ever, with innovations like Bluetooth 6.0, LE Audio, and Auracast™ shaping how devices connect and communicate.
This article explores Bluetooth Technology in depth, covering its history, modern applications, key devices, and what the future holds. You will see why it continues to be an essential part of our digital lives.
The Basics of Bluetooth Technology
Bluetooth is a short‑range wireless system. It lets two devices connect without cables. You use it in phones, laptops, speakers, watches, and even medical tools.
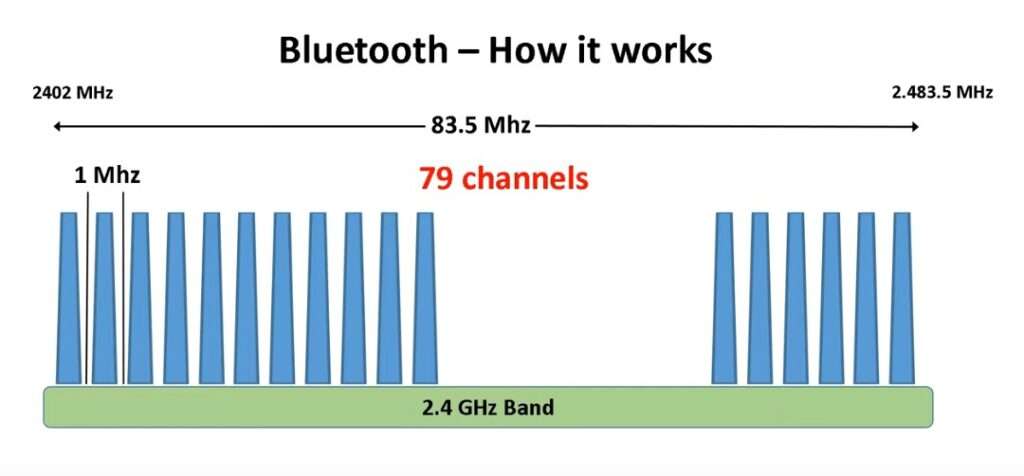
It works in a simple way. Devices send small signals through radio waves. The signals keep “hopping” between channels. This makes them stable and less likely to clash with Wi‑Fi.
Here’s why Bluetooth is so common:
- Uses very little energy.
- It works across many brands.
- It connects fast with no wires.
Modern versions add even more. They conserve battery life, minimize delays, and enable you to connect multiple devices simultaneously. That is why Bluetooth has become a global standard for wireless connections.
A Brief History of Bluetooth Technology
Bluetooth started in 1994 at Ericsson. The plan was simple: make a wireless replacement for serial cables.
The name comes from King Harald “Bluetooth” Gormsson of Denmark. He united tribes in the 10th century. The technology was meant to unite devices in the same way.
Classic Bluetooth vs. Low Energy
Early versions were called Classic Bluetooth. They allowed file transfers and music streaming. They worked well, but drained more power.
In 2010, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) arrived. This version changed the game. It lets trackers, sensors, and wearables run for months on tiny batteries.
Later came LE Audio. Added in 2019, it gave better sound and longer battery life. For hearing aids and wearables, this was a major step forward.
Key Milestones
- 1999: Bluetooth 1.0 – basic pairing and simple transfers.
- 2004: Bluetooth 2.0 – faster data and improved power efficiency.
- 2010: Bluetooth 4.0 – BLE for wearables and IoT devices.
- 2019: Bluetooth 5.0 – more range, faster speed, broadcast features.
- 2021–2023: Bluetooth 5.2–5.4 – LE Audio, Auracast™, better IoT tools.
- 2024–2025: Bluetooth 6.0 – precise positioning and smarter audio.
How Does Bluetooth Work?
Bluetooth sends data with short radio signals. Devices connect only at close range.
The signal does not stay on one channel. It keeps jumping from channel to channel. This avoids clashes with Wi‑Fi and other signals.
Because of this, Bluetooth stays steady. Even in busy areas, the link feels smooth and clear.
Types of Bluetooth Technology
Bluetooth comes in two main forms. Both are common today.
Bluetooth Classic
This is the original version of Bluetooth.
It works well for fast data.
People use it for music, calls, and file sharing.
The downside? It uses more power and drains batteries faster.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
BLE was added with Bluetooth 4.0.
It was designed to save battery life.
That makes it a good fit for fitness bands, watches, and sensors.
It uses less power and still works with Bluetooth Classic devices.
The Evolution of Bluetooth Technology
Bluetooth technology has undergone significant evolution over the years, revolutionizing the way we connect and communicate wirelessly. This evolution has seen Bluetooth technology continuously improve in speed, range, and efficiency to meet the demands of modern connectivity.
Bluetooth 6.0: The Next Leap
Bluetooth 6.0, ratified in August 2024, brings transformative improvements beyond faster speeds. Key features include:
- Channel Sounding: Precise indoor positioning to centimeter-level accuracy without UWB.
- Advanced Audio Handling: Supports LE Audio, Auracast™, and multipoint connections.
- Energy Efficiency: Smarter power management for IoT devices and wearables.
Real-World Devices
- Google Pixel Watch 3 – supports channel sounding for indoor navigation.
- Apple AirPods Pro 3 – leverage LE Audio for improved battery life and spatial audio.
- Samsung Galaxy Buds 3 – Auracast™ compatible for public audio broadcasts.
Bluetooth 6.1 and Future 6.2
Bluetooth 6.1 (2025) enhances the accuracy and reliability of channel sounding, making it suitable for retail, logistics, and crowded venues. Meanwhile, 6.2 will focus on:
- Dynamic spectrum management to reduce interference.
- Massive IoT device support for smart cities.
- Optimized audio streaming for low-latency gaming and AR/VR applications.
LE Audio & Auracast™: Redefining Wireless Sound
LE Audio introduces the LC3 codec, improving sound quality while reducing power consumption. It allows simultaneous audio streams to multiple devices—perfect for shared listening experiences.
Auracast™ enables broadcast audio: public venues like airports, gyms, or museums can transmit audio to multiple headsets simultaneously. It’s also transforming accessibility for hearing-impaired individuals.
Channel Sounding: A Game Changer
Channel sounding allows Bluetooth devices to measure signal timing and determine distances accurately. This capability is critical for:
- Indoor navigation in large complexes.
- Asset tracking in warehouses.
- Proximity marketing in retail spaces.
Brands like Nordic Semiconductor and Qualcomm are rolling out chips with built-in support, helping devices like the Pixel Watch 3 or Fitbit Charge 7 achieve precision tracking without extra hardware.
Applications of Bluetooth Technology: From Headsets to Smart Homes
Bluetooth is part of daily life. We use it for music, work, health, and even our homes. Its flexibility makes it one of the most common wireless tools in the world.
Wireless Audio Streaming
Wireless audio is the most familiar example. Headphones, earbuds, and car stereos all use Bluetooth. They let us stream music, take calls, and enjoy sound without messy cables.
Peripheral Device Connectivity
It also connects computer accessories. Keyboards, mice, and printers link quickly without adapters. This makes setup simple and clutter‑free.
Smart Home Automation
In smart homes, Bluetooth powers lights, locks, and thermostats. These devices can be controlled from a phone or even by voice, adding both convenience and energy savings.
Health and Fitness Tracking
Wearables and health tools also depend on it. Smartwatches and fitness bands track steps, heart rate, and sleep, then send the data to an app. Even medical sensors use Bluetooth to share important health details.
IoT (Internet of Things) Connectivity
Bluetooth powers countless IoT applications, including:
Mesh Networks: Buildings use Bluetooth Mesh for smart lighting, HVAC control, and occupancy tracking.
Retail: Electronic shelf labels using Bluetooth 5.4’s PAwR feature for real-time updates.
Smart Home: Bulbs (Philips Hue, GE Cync), thermostats, locks, and sensors rely on low-power Bluetooth.
Healthcare: Glucose monitors (Dexcom G7), blood pressure monitors, and hearing aids stream data to smartphones and tablets.
Key Features of Bluetooth Technology
Bluetooth technology has revolutionized the way we connect and share data wirelessly. Let’s explore some of the key features that make it such a sought-after technology.
Wireless Connectivity
One of the primary advantages of Bluetooth is its wireless connectivity, which allows devices to communicate and share data without the need for physical cables.
This feature enables seamless connections between devices, such as smartphones, laptops, headphones, and speakers, making it incredibly convenient for users.
Low Energy Consumption
Another standout feature of Bluetooth is its low energy consumption, which contributes to extended battery life for connected devices.
This energy-efficient technology is particularly beneficial for IoT devices, wearables, and other portable gadgets that rely on battery power, allowing for prolonged usage without frequent recharging.
Security & Privacy
Bluetooth has strengthened its security over time:
- Encrypted Advertising Data in Bluetooth 5.4 prevents spoofing.
- Improved authentication and key refresh in Bluetooth 6.0 reduce attack risks.
- Firmware updates from brands like Apple, Samsung, and Qualcomm patch known vulnerabilities.
Despite improvements, older devices remain vulnerable, so updating hardware and software is critical.
Market Trends & Forecasts
Bluetooth continues to dominate wireless connectivity. Key numbers for 2025:
- 7.5 billion units shipped globally, including wearables, smartphones, and IoT devices.
- IoT growth: Smart buildings and logistics are driving the adoption of Bluetooth Mesh.
- Wearables: Apple, Samsung, and Fitbit lead the U.S. market, leveraging LE Audio and Auracast™.
Seasonal peaks in search and sales often occur around November and May, coinciding with product launches and holiday shopping.
Competing Technologies
Bluetooth faces competition from:
- UWB (Ultra Wideband): Used for high-precision tracking, but more costly.
- Wi-Fi 6E/7: Higher throughput but higher power consumption.
- NearLink: Emerging in China for low-latency audio and IoT use cases.
However, Bluetooth’s ubiquity, low power usage, and backward compatibility keep it ahead.
Bluetooth in Windows 11
Windows 11 has improved Bluetooth audio quality with:
- Support for LE Audio devices.
- Super Wideband Stereo (SWS) mode for crisp audio even during voice calls.
- Improved pairing reliability with multiple devices.
This benefits PC gamers, office professionals, and multimedia users.
Bluetooth Device Examples
- Apple AirPods Pro 3: LE Audio, Auracast™, spatial audio.
- Samsung Galaxy Buds 3: Auracast™, low-latency gaming mode.
- Google Pixel Watch 3: Channel sounding for precise tracking.
- Fitbit Charge 7: Bluetooth 6.0, efficient wearable connectivity.
- Philips Hue Smart Bulbs: Bluetooth Mesh support for home automation.
Practical Tips for Users
- Keep Bluetooth firmware updated to improve security.
- Use LE Audio-enabled devices for better battery life.
- Leverage Auracast™ in public venues for shared audio experiences.
- Pair devices strategically to avoid interference in crowded areas.
Impact of Bluetooth Technology on Industries
Bluetooth technology has changed the way many industries work. It allows devices to talk to each other wirelessly, using very little energy. It is safe, fast, and works with many types of devices.
Automotive Industry
Cars now use Bluetooth to make driving safer and easier. Drivers can make hands-free calls and listen to music or podcasts without wires. Bluetooth also connects smartphones to navigation systems, giving real-time traffic updates and voice commands.
Healthcare and Wearable Technology
Bluetooth powers devices like fitness trackers, smartwatches, and medical monitors. These devices track heart rate, activity, and sleep. They send the data to phones or healthcare systems so doctors can watch patients even from far away. People can also use the data to improve their own health.
IoT and Smart Devices
Bluetooth helps smart home and industrial devices work together. Lights, locks, thermostats, and sensors can all connect wirelessly. Factories and warehouses use Bluetooth to track items and control systems automatically.
Future Possibilities for Bluetooth Technology
Bluetooth technology keeps improving, bringing new ways for devices to connect and work together. These changes will make life easier for users and help industries run more efficiently.
Bluetooth Mesh Networking
Bluetooth mesh allows many devices to connect in one large network. This helps smart homes, offices, and factories share information over long distances. Devices can talk to each other reliably, making automation smoother and more useful.
Better Audio Quality
New Bluetooth audio technology delivers clearer sound and lower delays. Headphones, speakers, and hearing aids can now provide better music, calls, and immersive experiences. Wireless audio is becoming almost as good as wired connections.
5G Integration
Combining Bluetooth with 5G makes devices faster and more responsive. This helps with real-time applications like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and smart devices that need quick responses. It also allows more devices to work together at once.
What’s Next
- Bluetooth 6.2+ will save more power and support large IoT networks.
- Shared audio will let people listen together in public places like gyms and airports.
- Better positioning may replace UWB for accurate location tracking in devices.
- Smart homes, health wearables, and factories will continue to grow with improved Bluetooth.
Bluetooth is no longer just for connecting gadgets. It is shaping the way we live, work, and use technology every day.
Frequently Asked Questions about Bluetooth Technology
What Is The Bluetooth Technology?
Bluetooth technology is a wireless communication system that allows devices to connect and exchange data. It operates on short-range radio waves, enabling hands-free calling, music streaming, and file sharing between compatible devices.
This technology is integrated into smartphones, headphones, speakers, and other electronic gadgets for seamless connectivity.
What Are The Features Of Bluetooth?
Bluetooth features include wireless connectivity, short-range communication, compatibility with various devices, low power consumption, and ease of use for data transfer and audio streaming.
It enables devices such as smartphones, headphones, and speakers to connect and communicate wirelessly without the need for cables.
What Means Bluetooth?
Bluetooth is a wireless technology that allows for short-range communication between devices. It enables data transfer, like files and audio, without cables.
What Are The Features Of Bluetooth Signals?
Bluetooth signals have a range of up to 100 meters, making them ideal for short-range wireless communication. They use low power and can connect multiple devices simultaneously. Bluetooth signals can transmit data, audio, and control commands, providing versatile connectivity options.
Conclusion
Bluetooth Technology has come a long way since its origins in the 1990s. From basic wireless connectivity to LE Audio, Auracast™, and precise indoor positioning, it remains the backbone of countless devices and systems in the U.S. and worldwide.
As Bluetooth 6.0 and beyond continue to roll out, expect smarter, faster, and more versatile wireless experiences—powering not just entertainment but health, industry, and connectivity at every level.
The bottom line: Bluetooth isn’t just a convenience anymore. It’s an essential technology shaping the way we live, work, and interact with the digital world.

A passionate tech blogger and the founder of Best Tech View, a dynamic platform dedicated to all things technology. With a keen interest in the tech, Ahmad strives to provide insightful and engaging content on the latest tech trends, and breakthroughs.